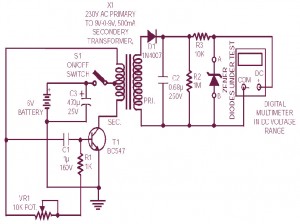
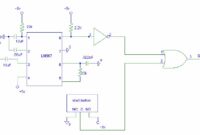
This is the circuit diagram of zener diode tester which tests zener diodes with breakdown voltages extending up to 120 volts. This is a handy circuit and will help you to measure the zener diode easily. This diode zener tester can be fitted in a 9V battery box. 1/3 of the box may be used for four 1.5V batteries and the remaining 1/3 is sufficient for accommodating this circuit.
The circuit has main advantage that it works with a voltage as low as 6V DC and consumes less than 8 mA electric current. In this circuit a commonly available center tap transformer with 230V AC primary to secondary 9-0-9V, 500mA secondary is used in reverse to achieve higher AC voltage across 230V AC terminals. Transistor T1 (BC547) is configured as an oscillator and driver to achive required AC voltage across transformer’s 230V AC terminals. This AC voltage is converted to DC by diode D1 and filter capacitor C2 and is used to test the zener diodes. R3 is utilized as a series current limiting resistor.
After assembling the circuit of zener diode tester, check DC voltage across points A and B without connecting any zener diode. Now switch on the S1 switch. The DC voltage across A-B should vary from 10V to 120V by adjusting potmeter VR1 (10k). If every thing is all right, the circuit is ready for use. For testing a zener diode of unknown value, connect it across points A and B with cathode towards A. Adjust the potensiometer of VR1 so as to achive the maximum DC voltage across A and B. Note down this zener value corresponding to DC voltage reading on the digital multimeter. When testing zener diode of value less than 3.3V, the meter shows less voltage instead of the actual zener value. However, correct reading is obtained for zener diodes of value above 5.8V with a tolerance of ? 10%. In case zener diode shorts, the multimeter will show 0 volts.